Software
Installation and setup
The SMD4 is compatible with the AML Device Control software, which can be downloaded from the Software page on our website: https://arunmicro.com/documents/software/
- Connect all SMD4 devices to your computer
If you intend to ultimately connect via LAN or Serial, start off by using the USB interface to perform basic setup on the LAN or serial interface first, then once satisfied connect on LAN or Serial as required.
Multiple instances of the same physical SMD4, but on different interfaces are allowed. For example, you could plug in the SMD4 with a network cable and USB lead, add the device connected via USB, configure network settings, then add device again as a network device. This can be useful during commissioning in establishing a working setup.
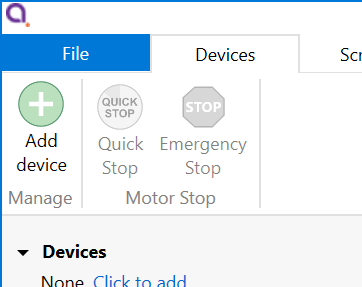
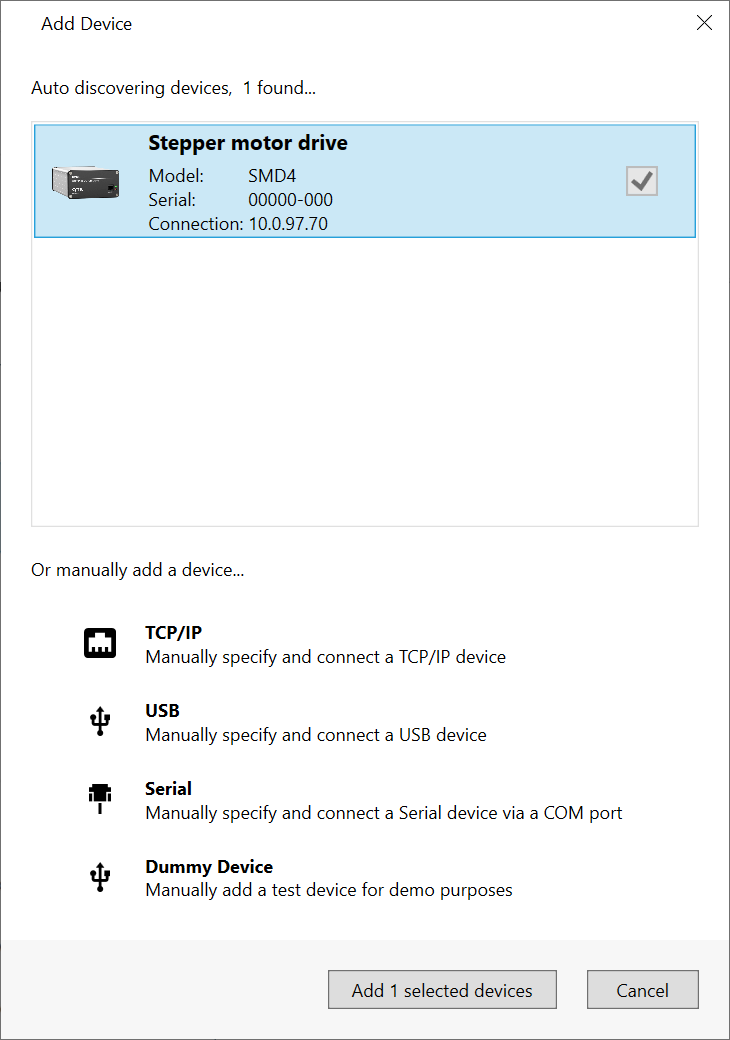
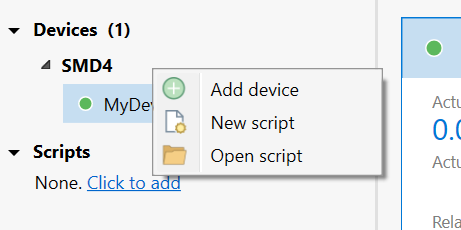
Note that the LAN interface only allows one connection at a time; auto-discovery of network connected device will fail to discover a device that is always connected to another software instance, be it AML Device Control or any other software. - Start the AML Device Control software and click ‘Add device’ in the top left corner
Connected SMD4 devices should automatically appear in the list. Select all devices that you wish to add and click “Add n selected devices”
The speed of auto detection varies by interface quantity of ports on your PC. Detection of USB and LAN devices is typically quick, whereas detection of devices connected via RS232 or RS485 can be considerably slower if a large number of COM ports are present on the PC.
The SMD4 network interface has an implementation of SSDP (Simple Service Discovery Protocol) which allows it to be discovered easily on a network, without knowing its IP address.
Overview
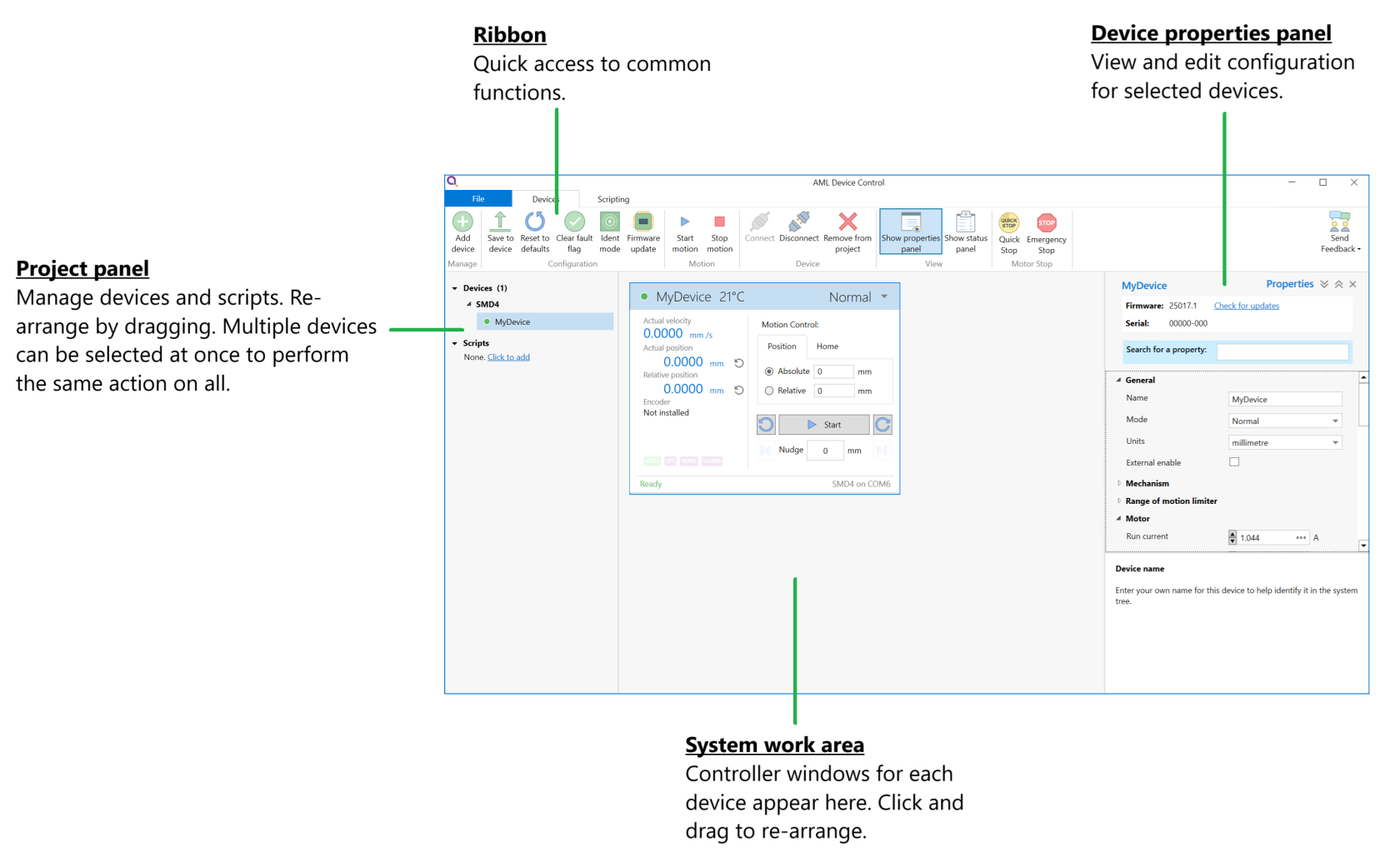
The default layout of the software is shown below:
Project panel
A status indicator next to each device shows the current status of each device according to these colours:
|
Colour |
Description |
|
|
Device connected and ready |
|
|
Bake mode running, limit switch triggered or joystick connected |
|
|
Device in a fault state |
|
|
Device disconnected |
Device properties panel
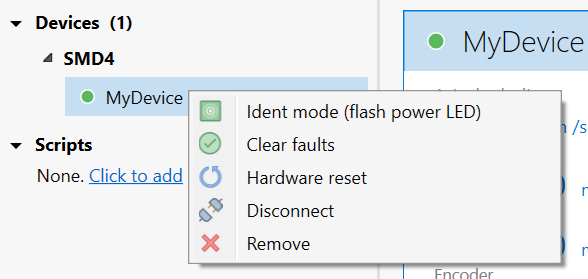
Select one or more devices in the project panel; their properties are displayed and can be edited here. A blank is shown for properties which are different across the selected devices. As each property is selected, help text appears at the bottom of the panel describing the configuration option in more detail.
-
Some properties allow selection of one of several choices, for example, temperature sensor selection:

-
Others such as ‘Run current’ simply require a numeric value to be entered
-
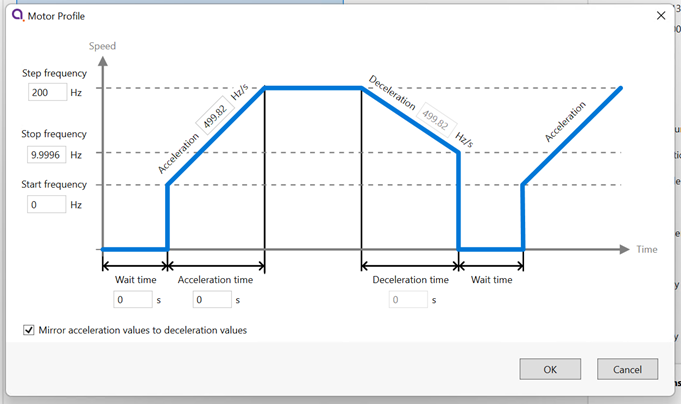
Others allow values to be entered directly, or the three dots button to the right to be clicked. This opens a window, allowing a more complex value to be input, for example, ‘Acceleration’ allows input in the native units or seconds:
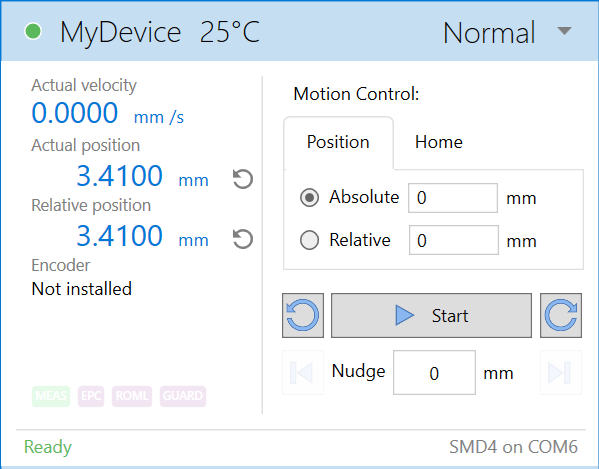
System work area
Controller windows for each device appear in this area. Windows can be arranged as desired and will automatically ‘snap’ to a grid making it easy to keep them neatly organised.
Controller window
Be aware that the synchronisation between multiple SMD4s is not specified or guaranteed. For example, if multiple devices are selected and the start button on the ribbon is clicked delays within the computer, software, and data connection to the SMD4 mean that each SMD4 will start or stop its motion at a slightly different moment, therefore this option is not suitable for performing complex co-ordinated movements across multiple axes.
Ribbon
Contains buttons for all actions. Hover over a button with the mouse to show tooltip with help information.
Scripting
Information on the available SMD4 device specific commands can be found in section USB of this manual. Serial command mnemonics will be auto completed by the script editor. The arguments of each scripting function are identical to those shown in section Command Reference, however, the format of querying and commanding is different. The example below shows how the SMD4 mode can be set and queried:
|
smd.Mode(1); smd.Mode(); |
// Set the SMD4 mode to 1 (Normal) // Query state of mode |
The ribbon contains scripting specific buttons.
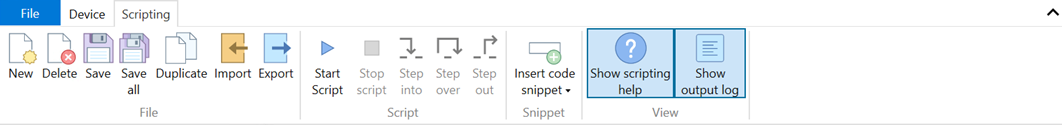
Utility functions
These utility functions don't translate to a command executed by the SMD4, and are used to perform tasks such as connecting devices, or creating delays in your program.
|
Function |
Description |
|
Add |
bool Add(string serial) Add a new device to the project. Returns true if the device has been detected and added to the project. serial: Device serial number. |
|
ClearLog |
void ClearLog( ) Clear command line. |
|
ConnectAll |
void ConnectAll( ) Connect all devices in the project. |
|
Delayms |
void Delayms(int value) Delay for a specified duration in milliseconds, before executing the next instruction. value: Minimum: 0 Maximum: 2^31 -1 |
|
DelaySeconds |
void DelaySeconds(int value) Delay for a specified duration in seconds, before executing the next instruction. value: Minimum: 0 Maximum: 2147483 |
|
DisconnectAll |
void DisconnectAll( ) Disconnect all devices in the project. |
|
Log |
void Log(string value) Print value to the command line. |
|
Name |
bool Name(string serial, string name) Change name of the device. Returns true if the device has been found and name changed. serial: Device serial number. name: Device new name. |
|
Remove |
bool Remove(string serial) Remove a device from the project. Returns true if the device has been detected and removed from the project. serial: Device serial number. |
|
RemoveAll |
void RemoveAll( ) Remove all devices from the project. |
|
Select |
bool Select(string[ ] devices) Returns true if all the requested devices have been selected. devices: Name of the device(s). |
|
SelectAll |
void SelectAll( ) Select all devices. |
|
SelectNone |
void SelectNone( ) Deselect all devices. |
Functions that query the SMD4 and that are not also available as a remote command are listed below.
Note that these all return an array rather than a single value, with each array element corresponding to the data from one SMD4. Use the array index syntax to access the desired element. This applies regardless of the number of devices.
For example, if there is only one SMD4 connected, use BakeActiveFlag()[0] to get the state of the bake active flag for that device.
The order of the array elements matches the order in which the SMD4 devices are selected. For example, suppose the “X-axis”, “Y-axis” and “Z-axis” named devices were selected with the command “smd.Select(“Z-axis”, ”X-axis”, ”Y-axis)”, to check the standby flag of the “Z-axis” device, use MotorStandbyFlag()[2]. Notice that array indices are 0 based.
|
Function |
Description |
|
BakeActiveFlag |
bool[] BakeActiveFlag() Returns true if the bake mode is running. |
|
ConfigurationErrorFlag |
bool[] ConfigurationErrorFlag() Returns true if the motor configuration is corrupt. |
|
EmergencyStopFlag |
bool[] EmergencyStopFlag() Returns true if the motor is disabled by software. |
|
ExternalEnableFlag |
bool[] ExternalEnableFlag() Returns true if the external enable input is high. |
|
ExternalInhibitFlag |
bool[] ExternalInhibitFlag() Returns true if the external enable input is disabling the motor. |
|
IdentModeActiveFlag |
bool[] IdentModeActiveFlag() Returns true if the ident mode is active. |
|
JoystickConnectedFlag |
bool[] JoystickConnectedFlag() Returns true if the joystick is connected. |
|
LimitNegativeFlag |
bool[] LimitNegativeFlag() Returns true if the negative limit is active. |
|
LimitPositiveFlag |
bool[] LimitPositiveFlag() Returns true if the positive limit is active. |
|
MotorOverTemperatureFlag |
bool[] MotorOverTemperatureFlag() Returns true if the motor temperature is greater than 190 °C. |
|
MotorShortFlag |
bool[] MotorShortFlag() Returns true if a motor phase to phase or phase to ground short has been detected. |
|
MotorStandbyFlag |
bool[] MotorStandbyFlag() Returns true if the motor is stationary. |
|
TargetVelocityReachedFlag |
bool[] TargetVelocityReachedFlag() Returns true if the motor is at the target step frequency. |
|
TemperatureSensorOpenFlag |
bool[] TemperatureSensorOpenFlag() Returns true if the selected temperature sensor is open circuit. |
|
TemperatureSensorShortedFlag |
bool[] TemperatureSensorShortedFlag() Returns true if the selected temperature sensor is shorted (not applicable to thermocouple) |


 icons adjacent to the readouts.
icons adjacent to the readouts.